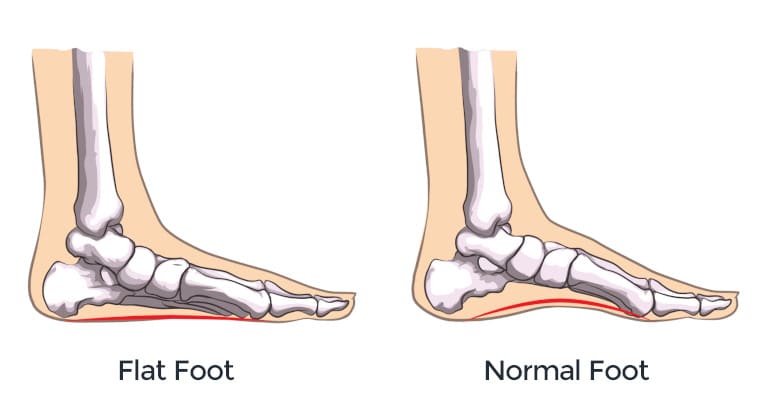
Platypodia (flat feet) is a quite common problem. In children, valgus platypodia is diagnosed during physical examination in 70% of cases. At the same time, it cannot be always treated with help of conservative methods of treatment. At Ladsiten, platypodia in children and adults is corrected using modern osteotomy and the Veklich fixation device.
What is platypodia

Platypodia in children and adults is a type of foot deformity. Its other names are “valgus foot” and “flat valgus foot”. According to the generally accepted classification of diseases (ICD-10), platypodia is considered a congenital deformity (code Q66), but the genetic factor is not always the leading one. So, while discussing platypodia in children, Dr. Komarovsky points to the possibility of correcting the deformity, even if the parents have it.
A normal foot forms two physiological arches – the longitudinal and transverse ones. These are two peculiar “arches” that are present on the feet of any healthy person. In some situations, arches do not form and the foot remains flat.
Such a foot does not just change its appearance but affects the musculoskeletal system and joints. Against the background of platypodia, valgus deformity of the knees develops, the load is not distributed correctly. In the future, this can lead to arthrosis.
Often, patients with deformity complain of feeling pain in the foot and the inability to bear physical exertion. They are forced to wear special comfortable shoes instead of the stylish ones.
Types of platypodia
Platypodia is considered a physiological state in children up to 7 years of age. During this time, the foot is still forming. But if no progress can be seen in a child of 4-5 years old, this gives indications to take conservative supportive measures.
The classification of platypodia is done according to three characteristics, as follows:
According to localization:
- Longitudinal. The foot changes its appearance. It lies completely on the floor, making the legs bent inward. The arch is absent or not fully present.
- Transverse. In this case, the forefoot is expanded. The load is transferred to all metatarsal bones, instead of the first and fifth ones. Often, with this pathology, hallux valgus develops – that is, the well-known “bunion” on the thumb.
Combined platypodia in children includes both types of foot deformity.
According to the stage of development:
- Stage one. The absence of the arch is weakly expressed. Legs may swell and hurt after exercise.
- Stage two. Breaks the posture and causes severe pain, backache and “knocking” not only in the foot, but also in the ankle.
- Stage three. It is difficult for the patient to walk; the leg is completely deformed. Arthrosis and arthritis develop.
According to the cause:
- Traumatic;
- Paralytic;
- Acquired;
- Rickety;
- Static.
In terms of external appearance, all types of platypodia are similar. Visually, they differ only in severity.
Diagnostics
Platypodia in children: how to determine it without a doctor? Impatient parents often ask themselves about it. At home, you can carry out a simple test. Wet your baby’s foot, sponge it up a little with a towel. Then place the foot on a flat surface; you can also put it on paper. Now you need to check the footprint: if it has acquired a normal shape with a lateral notch, then there is no pathology. At polyclinics, doctors similarly make a footprint to determine platypodia in children.
The test is not 100% indicative. Do not get your child self-diagnosed. Modern X-ray equipment and a doctor’s examination make it possible to determine the presence of pathology accurately. An X-ray is done for both feet in a direct and lateral projection with a load. In some cases, an MRI is prescribed.
At Ladisten, you can get a detailed consultation from an orthopedist and undergo high-quality instrumental diagnostics.
Causes of the pathology
Platypodia in children is a part of natural physiology. In childhood, it is formed due to a “cushion” on the foot. In the process of formation of the musculoskeletal system and bone growth, the cushion disappears and its place is occupied by an arch. True congenital platypodia is rarely determined, but it can be seen on X-rays. At the heart of heredity lies the peculiarity of elasticity of the capsular ligament apparatus.
The main causes of valgus foot formation include¹:
- Platypodia in children whose weight exceeds the norm. Excess weight contributes to improper load distribution;
- Disorder in the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus, rickets. If the bones soften, they cannot hold the body so that it “sags”, literally falling on the feet with all its weight;
- Paralytic diseases, such as poliomyelitis, encephalitis;
- Neurology. For example, fetal hypoxia at birth;
- Long wearing of uncomfortable shoes;
- Injuries and fractures of the calcaneus and ankle.
Preventive measures
How to prevent platypodia in a child if he or she has poor heredity? In this case, you need to use orthopedic shoes from an early age. These include boots and sandals with a high back and arch support. It is better to make such shoes to order – then they are selected according to the parameters of a particular child. In no case should your child wear shoes after someone!
A balanced physical activity is needed. It’s good to for the child to take swimming. Additionally, he or she can walk on a special rug with pebbles.
It is important to ensure a proper diet. Calcium, vitamin D and phosphorus are really necessary to form a normal musculoskeletal system and prevent rickets.
Do not forget about vaccination, as poliomyelitis has serious consequences. It is better to get vaccinated.
The main thing to understand is that prevention of platypodia in children is possible only up to a certain age. If you miss the moment, it becomes useless.
Treatment

Physiological platypodia in children does not require treatment up to 4 years. If the foot has not taken a normal shape at this age, platypodia in children is medically supervised and initial conservative measures are taken. This includes wearing of orthopedic insoles, arch support, special gymnastics. The situation can get right by the age of 7 years.
Unfortunately, after 7-8 years, platypodia can no longer be treated conservatively. The pathology can progress so that platypodia is developed in a teenager, bringing a lot of trouble. Then surgical treatment is indicated.
There is a way to correct the disease using special titanium implants. In practice, it causes complications, the pain may not go away for up to 3 months², and as a result, the implants are removed.
Osteotomy performed using the Ilizarov apparatus³ shows a favorable outcome in most cases. At Ladisten, an improved design, that is, the Veklich device, is used for the treatment of platypodia. The rehabilitation period with it is shorter, and the operation itself is minimally invasive and does not take more than 40 minutes.
Sourses
¹ Children’s surgery. National leadership. Russian Association of Pediatric Surgeons. National project “Health”. Ed. Yu.F. Isakova, A.F. Dronova. Moscow 2009 1168 p.
²Tamoev Sargon Konstantinovich, Zagorodni Nikolay Vasilievich, Protsko Victor Gennadevich, Sultanov Elmar Maisovich, Khamokov Z.Kh., and Butaev Butay Gaidarovich. “Analysis of complications after subtalar arthroeresis in patients with flat valgus deformity of the feet” Traumatology and Orthopedics of Russia, no. 4, 2011, pp. 37-43.
³ Sergey Zyryanov, Yury Petrovich Soldatov, and Sergey Yakovlevich Zyryanov. “Surgical treatment of patients with post-traumatic flatfoot using the Ilizarov apparatus” Orthopedics genius, no. 3, 2011, pp. 38-41.
Ladisten
Average rating: 0 reviews 

 Ru
Ru Uk
Uk